What Kind Of Shareholders Own L.B. Foster Company (NASDAQ:FSTR)?

Every investor in L.B. Foster Company (NASDAQ:FSTR) should be aware of the most powerful shareholder groups. Institutions will often hold stock in bigger companies, and we expect to see insiders owning a noticeable percentage of the smaller ones. I generally like to see some degree of insider ownership, even if only a little. As Nassim Nicholas Taleb said, 'Don’t tell me what you think, tell me what you have in your portfolio.'
With a market capitalization of US$276m, L.B. Foster is a small cap stock, so it might not be well known by many institutional investors. Taking a look at our data on the ownership groups (below), it's seems that institutional investors have bought into the company. Let's delve deeper into each type of owner, to discover more about FSTR.
View our latest analysis for L.B. Foster
What Does The Institutional Ownership Tell Us About L.B. Foster?
Institutional investors commonly compare their own returns to the returns of a commonly followed index. So they generally do consider buying larger companies that are included in the relevant benchmark index.
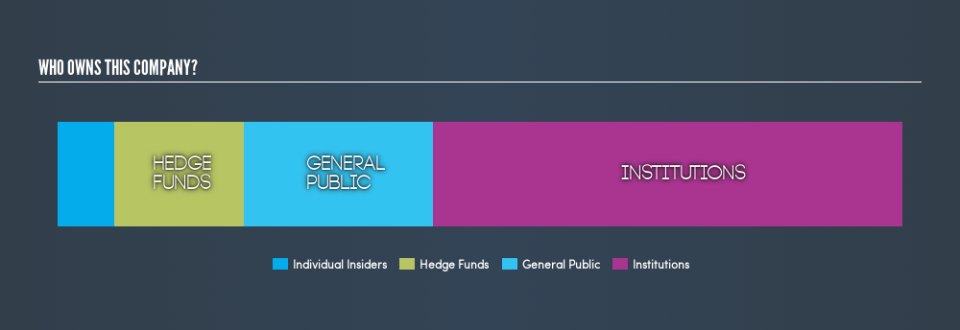
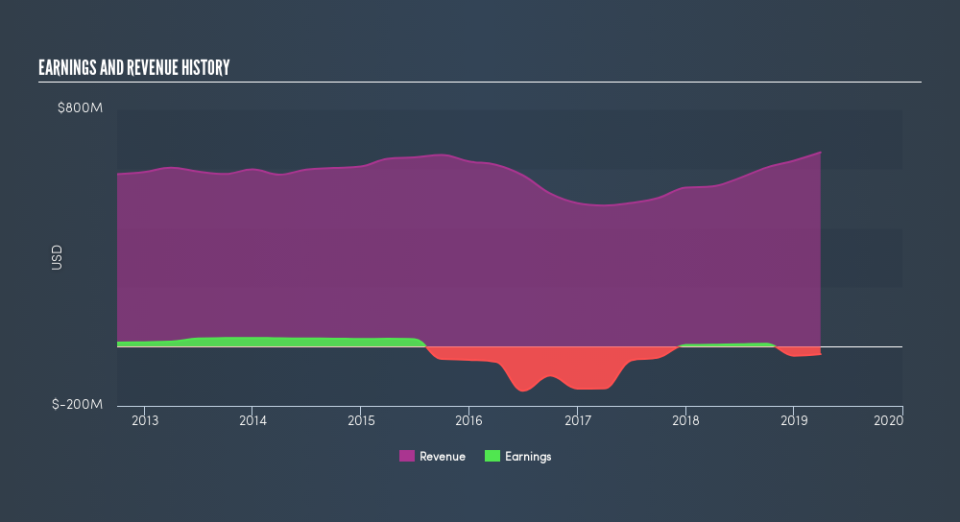
L.B. Foster already has institutions on the share registry. Indeed, they own 55% of the company. This suggests some credibility amongst professional investors. But we can't rely on that fact alone, since institutions make bad investments sometimes, just like everyone does. When multiple institutions own a stock, there's always a risk that they are in a 'crowded trade'. When such a trade goes wrong, multiple parties may compete to sell stock fast. This risk is higher in a company without a history of growth. You can see L.B. Foster's historic earnings and revenue, below, but keep in mind there's always more to the story.
Institutional investors own over 50% of the company, so together than can probably strongly influence board decisions. Our data indicates that hedge funds own 15% of L.B. Foster. That catches my attention because hedge funds sometimes try to influence management, or bring about changes that will create near term value for shareholders. While there is some analyst coverage, the company is probably not widely covered. So it could gain more attention, down the track.
Insider Ownership Of L.B. Foster
The definition of an insider can differ slightly between different countries, but members of the board of directors always count. The company management answer to the board; and the latter should represent the interests of shareholders. Notably, sometimes top-level managers are on the board, themselves.
Most consider insider ownership a positive because it can indicate the board is well aligned with other shareholders. However, on some occasions too much power is concentrated within this group.
We can see that insiders own shares in L.B. Foster Company. In their own names, insiders own US$19m worth of stock in the US$276m company. Some would say this shows alignment of interests between shareholders and the board. But it might be worth checking if those insiders have been selling.
General Public Ownership
The general public, with a 22% stake in the company, will not easily be ignored. While this size of ownership may not be enough to sway a policy decision in their favour, they can still make a collective impact on company policies.
Next Steps:
While it is well worth considering the different groups that own a company, there are other factors that are even more important.
I like to dive deeper into how a company has performed in the past. You can access this interactive graph of past earnings, revenue and cash flow, for free .
If you would prefer discover what analysts are predicting in terms of future growth, do not miss this free report on analyst forecasts.
NB: Figures in this article are calculated using data from the last twelve months, which refer to the 12-month period ending on the last date of the month the financial statement is dated. This may not be consistent with full year annual report figures.
We aim to bring you long-term focused research analysis driven by fundamental data. Note that our analysis may not factor in the latest price-sensitive company announcements or qualitative material.
If you spot an error that warrants correction, please contact the editor at editorial-team@simplywallst.com. This article by Simply Wall St is general in nature. It does not constitute a recommendation to buy or sell any stock, and does not take account of your objectives, or your financial situation. Simply Wall St has no position in the stocks mentioned. Thank you for reading.

 Yahoo Movies
Yahoo Movies